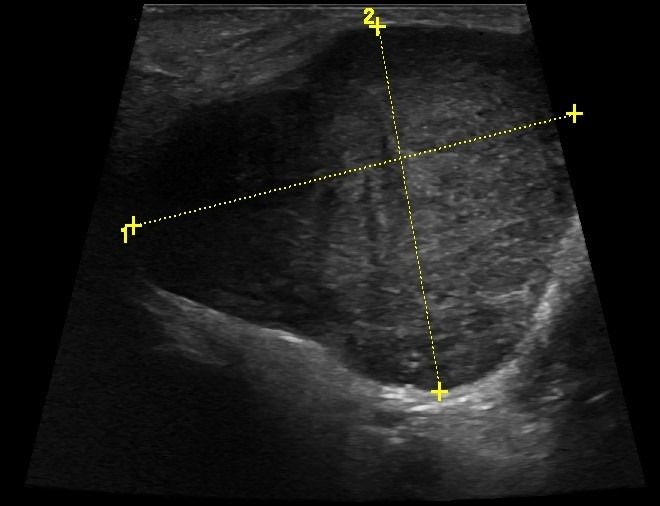
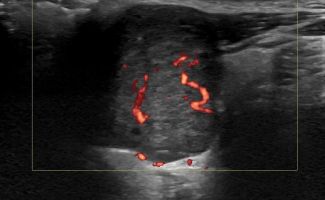
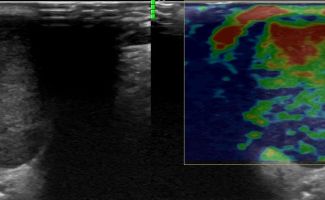
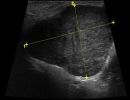
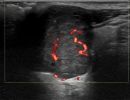
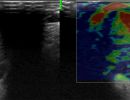
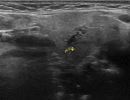
What pathologies can be diagnosed with Ultrasound of Salivary Glands?
High-resolution Color Doppler Ultrasound with Elastography can reliably diagnose pathologies such as:
- Detection of stones and Dilatation of the excretory ducts and in the context of sialolithiasis and sialadenitis
- Autoimmune diseases, such as Sjogren's syndrome
- Focal lesions, such as tumors (pleomorphic adenoma, Warthin's tumor, lymphoma)
- Enlarged intraglandular lymph nodes
How is the reliability of the diagnosis ensured with Ultrasound of Salivary Glands?
The reliability of Ultrasound in diagnosing Salivary Gland pathologies has been established in recent years. It is ensured by using state-of-the-art ultrasound machines with specialized high-frequency probes and the familiarity and experience of the examiner-radiologist with the sonoanatomy and pathology of Salivary Glands and the head-neck region.
How is the Ultrasound of Salivary Glands performed?
The patient lies down in a supine position, and the doctor applies gel to the area. Using a specialized high-resolution ultrasound probe, the doctor examines the Salivary Glands (Parotid and Submandibular Glands). The Ultrasound of Salivary Glands is a painless examination and does not require any specific preparation. The duration of the examination is 20-30 minutes.