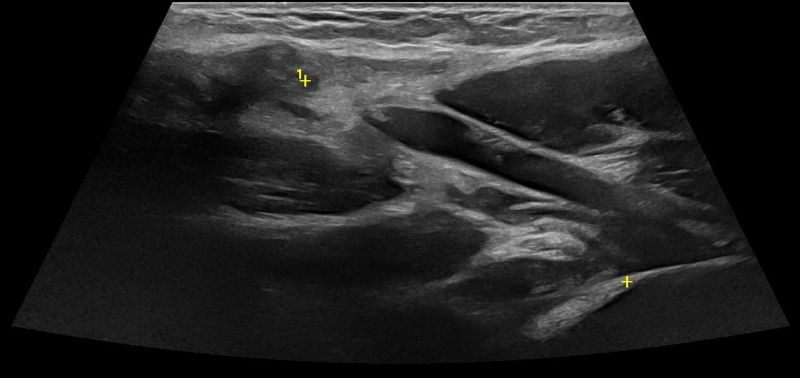
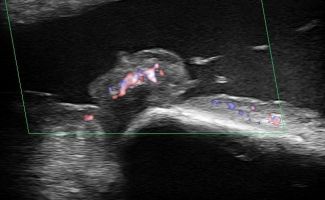
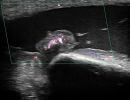
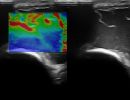
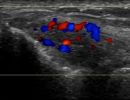
What can be diagnosed with Elbow Ultrasound?
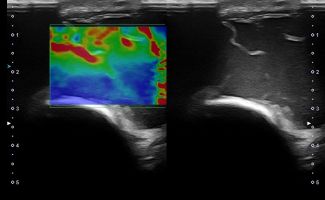
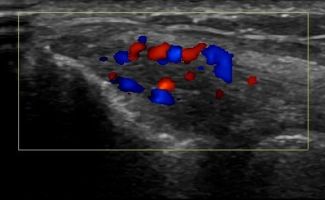
Elbow Ultrasound provides comprehensive imaging of various structures in the region, allowing the identification of pathologic conditions in the joint, bursae, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and soft tissues of the elbow.
Elbow Joint
- Fluid collection in the elbow joint (i.e. hemarthrosis)
Elbow Bursae
- Fluid collection in the bursa (i.e olecranon bursitis)
- Synovitis in the bursa as a symptom of Rheumatologic Disease
Elbow Tendons
- Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow)
- Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow)
Elbow Ligaments
- Partial or complete tear of the medial/lateral collateral ligament
Elbow Nerves
- Ulnar Neuritis
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
Elbow Soft Tissues
- Ganglia
- Lipomas
- Tumors
- Enlarged lymph nodes
What are the advantages of Elbow Ultrasound compared to other imaging methods?
-
Dynamic Testing: Ultrasound is inherently a dynamic imaging method, meaning that the examination and diagnosis can occur during movement. This capability is particularly important for Elbow Ultrasound, allowing a comprehensive examination of the area in various positions and movement points.
-
Patient-Friendly Examination: Elbow Ultrasound is a patient-friendly examination, as it does not involve the administration of intravenous drugs, magnetic resonance coordination, or exposure to ionizing radiation.
How is Elbow Ultrasound performed, and what preparation does it require?
Elbow Ultrasound is a simple and painless process. Gel is applied to the patient's skin, and using the transducer, the doctor examines the elbow area. During the examination, the patient remains seated and performs various movements as directed by the doctor to dynamically assess the area. The duration of the ultrasound scan is approximately 20-30 minutes.